7-Keto enables the body to build muscle in a growth
promoting environment.* It may also increase your body's ability to burn
calories.* It is a non-hormonal, non-androgenic derivative of DHEA.
The groundbreaking new micronutrient 7-Keto, a patented compound which, by
activating thermogenic enzymes, "revs up" the basal metabolic rate and thus
"burns" calories more rapidly and continually throughout the day, even while
resting, as well as inhibit the storage of fat within the body.*
All About 7-Keto
When we age the
ability to control our quality of life becomes an issue for all of us. The
application of aging research into the steroid dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) has
helped our understanding of age induced losses of functional capacity, and has
subsequently lead to the discovery of a relatively new compound "7-OXO-DHEA".
7 - Keto as it is more commercially known may have physiological actions that
allow us to train well into old age. Recent studies suggest it may also have
applications to a youthful, healthy, and physically active population. So the
questions beckon; is there evidence to support 7-keto use over a broad spectrum
of ages? And if so, how can it affect our physiques? And what lessons can be
learned from ageing science to keep us ahead of the dietary supplement market
regarding the use of this novel compound?

The Scientific Facts Behind 7-Keto
DHEA

The appliance of science to any functional context, in this case your health,
performance and physique goals, are the mark of any good nutritional scientist.
But as a scientist you can only base your assumptions on the scientific facts
and fortunately for us this month we have plenty to work with; as the discovery
of the DHEA metabolite "3b -Acetoxyandrost - 5 - ene-7, 17- dione" was
discovered back in the late 1950's1 (and they wonder why we call it
7-Keto...imagine fitting that one on the label).
Because of this we have amassed a large volume of work in this often heavily
chemical orientated, and sometimes confusing area of metabolism. In the past,
7-keto's closest relative DHEA gave us the initial and
indeed pioneering insights into the potential benefits this class of compound
can deliver.
Although considered relatively inert by the mid to late 90's, this view on
DHEA was in for a radical change. The National Institute of Aging (web site) issued a public service
announcement regarding its safety and warned consumers of its sex steroid
associated side effects5. Because of the potential benefits to
health, the search for a DHEA-like compound without the associated side effects
was on. Although first identified in human urine in 19481 and tissues
in 19546 it wasn't until the mid 90's when Dr. Henry Lardy began the
excellent research on what he called "Ergosteroids"7.
The nomenclature of the ergosteroid family emerged due to their influences on
energy metabolism; indeed this area in particular will form the core of our
discussion on 7-keto. After a paper was released showing that DHEA could bring
about a thermoginetic effect in rats, it wasn't long before both the
nutraceutical and scientific world began the search for an effective and "safe
alternative to ephedrine" for fat loss. In essence, a chemical that could confer
the positive health benefits of DHEA.
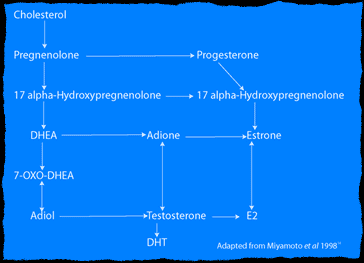
Fig.1 The biosynthetic pathway of 7-keto DHEA. Click To
Enlarge.
Feeding The Machine (Pharmacokinetics &
Safety)
DHEA is a steroid produced by the adrenal gland7 and is the most
abundant steroid in human blood8. There are always two things you
should understand prior to the use of any sport / health supplement.
- Safety of the product and the dose range proven to be safe.
- Knowledge of how the supplement is taken up into the tissues and how quick
it is excreted, "in-essence it's pharmacokinetic profile".
7-keto is a highly active derivative of DHEA and is one supplement of which
its pharmacokinetic profile is needed if we want to ascertain when peak levels
occur in plasma. This information will help prescribe the best possible rational
for its time of use, dosage, and safety to optimise body compositional changes.
A series of trials have looked at both the safety and pharmacokinetics of
7-keto (see Fig. 2 below.). In animal studies, 7-Keto was shown to be safe and
in effect non-toxic to levels of 2000mg/kg in rats9 and 1000mg/kg in
monkeys10. Toxicity was assessed by full-blood chemistry, blood cell
counts and histological examination in 42 different tissues. Again caution must
be taken until we see the human data; so what human data does exist? Davidson et
al11 studied a series of doses ranging from 50mg/d (25mg twice daily)
for 7 days; 100mg/d (50mg twice daily) for 7 days; and finally 200mg/d (100mg
twice for 28 days). Results demonstrated that at all doses, 7-keto in comparison
to a placebo presented no substantial impact on clinical blood markers of
toxicity and health. This data was supported in further human
trials12-13.